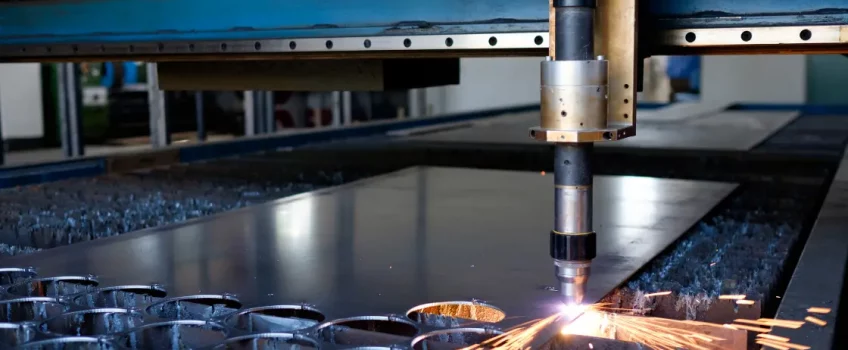
Plasma cutting has been in use since the 1960s and is still the preferred method for automotive repair shops, fabrication shops, industrial construction sites and salvage operations. This is largely due to the high speeds and precision cuts these machines can achieve.
While it was rather time-consuming and expensive in the early days, advancements in technology and engineering techniques made it a more user-friendly, economical and productive method. In this article, we discuss different plasma cutting methods, how it works, some of the applications and pros and cons.
How Does A Plasma Cutter Work?
Modern, high-end plasma cutters use compressed air and special gas to produce a plasma reaction. It is this process that allows the machine to cut through a wide range of metals including the following:
- Aluminium
- Mild steel
- Stainless steel
- Carbon steel
- Copper
- Brass
- Expanded steel
Plasma Cutting Processes
Today, plasma cutting is more widely used and unlike conventional “metal against metal” processes, it doesn’t produce metal chips. This means it can create more accurate cuts for a better finish. Before we go any further, let’s take a look at three major processes used for plasma cutting:
Air Plasma Cutting
This particular process usually employs a hand-torch for cutting metal, which is the most portable plasma cutting option. It predominantly uses inverter power supply technology and has these additional key features:
- The system can run within a power output range of 12 amps to 120 amps
- Cutting thicknesses as low as 1/8 inch
Mechanised Plasma Cutting
Many companies, including shipyards and steel service centres, use this system because of its high productivity. Its most notable features include the following:
- Uses machine-mountable torches
- Available in amperages ranging from 130 amps to 1,000 amps
- Cutting thicknesses of up to 61⁄4 inches
- It requires constant manual monitoring of different factors, such as gas flow, pressure, arc voltage
High Definition Plasma Cutting
Since the 1990s, high-definition plasma cutting was the most viable metal cutting solution and has gone through numerous research and development phases since its inception. Some of the major benefits include:
- High-quality cuts
- Economical operating cost
- High cutting speeds
At first, it could cut metal with a thickness of 3⁄8 inches but with advancements in engineering technology, it can cut mild steel of 3 inches (75mm) at 400 amps and on stainless and aluminium, more than 6 inches or 150mm at 800 amps.
Some of the important features of this process are:
- To achieve the highest quality, plasma cutting requires monitoring by expert operators
- Cutting thicknesses can be as low as 26 gauge to as big as 3 inches. When used on carbon steel, a thickness capacity of up to 61⁄4 inch is also achievable
- It requires power levels ranging from 130 amps to 800 amps
- Technology updates on plasma cutting methods are continuing to evolve for better results in cut quality and productivity
What Thickness Can A Plasma Cutter Process?
A handheld plasma torch can usually cut through 38mm (1.5 inches) of steel plate while an industrial, computer-controlled device can sever 150mm (6 inches). Another factor to take into consideration is the type of metal you’ll be cutting as it could vary. For example, you can cut thicker pieces of mild steel a lot faster than with alloys.
It’s important to remember that the thicker a metal, the more hazardous the process can be. In many cases, sparks are produced so make sure you stay within your machine’s cutting capacity and follow all the necessary safety protocols when it comes to plasma cutting.
For more informative and interesting articles on waterjet cutting, CNC machining, shot blasting and emerging technologies, please read our blog and follow us on social media. You can also find all of our products and services on our website.


 Mail:
Mail: 



